RAG Evaluation with RAGAS and MLflow
- Why This Tutorial?
- What You'll Learn
- Prerequisites
- Setup and Configuration
- Sample Knowledge Base
- Minimal RAG Pipeline
- Load Golden Dataset
- RAGAS Evaluation with MLflow
- MLflow Results Analysis
- Common Pitfalls and Solutions
- Extras: Comparing RAG Variants with MLflow
- How to inspect results in MLflow UI:
- More from MLflow
- References, further reading
Why This Tutorial?
Evaluating RAG pipelines is surprisingly difficult. You can build a working retrieval system in an afternoon, but answering "Is it actually good?" requires systematic measurement.
The challenge: Manual evaluation doesn't scale. Eyeballing a few responses tells you almost nothing about overall quality. You need metrics that capture different aspects of RAG performance:
- Is the retriever finding relevant documents?
- Is the LLM staying faithful to the retrieved context (not hallucinating)?
- Are the answers factually correct?
The solution: RAGAS provides standardized metrics for RAG evaluation. MLflow provides experiment tracking. Together, they enable systematic, reproducible evaluation that you can run on every pipeline change.
What made this tricky: The MLflow-RAGAS integration looks simple in the docs, but getting it to work with a real LangChain pipeline required navigating several non-obvious requirements:
- Specific model URI formats for different providers
- Function signatures that match MLflow's expectations
- Proper tracing spans for context-aware metrics
This tutorial documents what actually works, including the gotchas I encountered along the way.
This tutorial demonstrates how to evaluate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems using RAGAS (Retrieval Augmented Generation Assessment) metrics through MLflow integration.
NOTE: RAGAS is a third-party evaluation library. For more details, visit the RAGAS GitHub repository. At the time of writing (January 2026), apart from RAGAS, MLFlow supports another third-party scorer/evaluation library: DeepEval.
What You'll Learn
- Build a minimal RAG pipeline using LangChain and FAISS
- Create a golden evaluation dataset with expected answers
- Evaluate RAG quality using RAGAS metrics (Faithfulness, Context Precision, Context Recall, Factual Correctness)
- Track results in MLflow for systematic comparison
- Support multiple LLM providers: OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Ollama
Prerequisites
- Python 3.10+
- API key for your chosen LLM provider
- Basic understanding of RAG concepts
import os
import warnings
from enum import Enum
import pandas as pd
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
LLM Provider Configuration
This tutorial supports three LLM providers. Choose your provider and configure the appropriate environment variables:
| Provider | Required Environment Variables |
|---|---|
| OpenAI | OPENAI_API_KEY |
| Azure OpenAI | AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT, AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY, AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME |
| Ollama | None (runs locally on http://localhost:11434) |
class LLMProvider(Enum):
OPENAI = "openai"
AZURE_OPENAI = "azure_openai"
OLLAMA = "ollama"
# === CONFIGURE YOUR PROVIDER HERE ===
PROVIDER = LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI
# Model names per provider
MODEL_CONFIG = {
LLMProvider.OPENAI: {
"chat_model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"embedding_model": "text-embedding-3-small",
},
LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI: {
"chat_model": os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME", "gpt-4o-mini"),
"embedding_model": os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_DEPLOYMENT", "text-embedding-3-small"),
},
LLMProvider.OLLAMA: {
"chat_model": "llama3.2:3b",
"embedding_model": "nomic-embed-text",
},
}
print(f"Using provider: {PROVIDER.value}")
print(f"Chat model: {MODEL_CONFIG[PROVIDER]['chat_model']}")
print(f"Embedding model: {MODEL_CONFIG[PROVIDER]['embedding_model']}")
Using provider: azure_openai Chat model: gpt-4o-mini Embedding model: text-embedding-ada-002-v2
def validate_environment(provider: LLMProvider) -> None:
"""Validate required environment variables for the selected provider."""
required_vars = {
LLMProvider.OPENAI: ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI: [
"AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT",
"AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY",
],
LLMProvider.OLLAMA: [],
}
missing = [var for var in required_vars[provider] if not os.getenv(var)]
if missing:
raise EnvironmentError(
f"Missing environment variables for {provider.value}: {missing}\n"
f"Please set them before continuing."
)
# Set provider-specific env vars for litellm (used by RAGAS scorers)
if provider == LLMProvider.OLLAMA:
os.environ.setdefault("OLLAMA_API_BASE", "http://localhost:11434")
print(f"OLLAMA_API_BASE set to: {os.environ['OLLAMA_API_BASE']}")
elif provider == LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI:
# Set litellm Azure env vars from Azure OpenAI vars
if os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY") and not os.getenv("AZURE_API_KEY"):
os.environ["AZURE_API_KEY"] = os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"]
if os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT") and not os.getenv("AZURE_API_BASE"):
os.environ["AZURE_API_BASE"] = os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"]
os.environ.setdefault("AZURE_API_VERSION", os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION", "2024-02-01"))
print(f"Azure litellm env vars configured")
print(f"Environment validated for {provider.value}")
validate_environment(PROVIDER)
Azure litellm env vars configured Environment validated for azure_openai
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings, AzureChatOpenAI, AzureOpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.embeddings import OllamaEmbeddings
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOllama
def get_llm(provider: LLMProvider):
"""Factory function to create LLM instance based on provider."""
config = MODEL_CONFIG[provider]
if provider == LLMProvider.OPENAI:
return ChatOpenAI(
model=config["chat_model"],
temperature=0,
)
elif provider == LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI:
return AzureChatOpenAI(
azure_deployment=config["chat_model"],
api_version=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION", "2024-02-01"),
temperature=0,
)
elif provider == LLMProvider.OLLAMA:
return ChatOllama(
model=config["chat_model"],
temperature=0,
base_url="http://localhost:11434",
)
def get_embeddings(provider: LLMProvider):
"""Factory function to create embeddings instance based on provider."""
config = MODEL_CONFIG[provider]
if provider == LLMProvider.OPENAI:
return OpenAIEmbeddings(model=config["embedding_model"])
elif provider == LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI:
return AzureOpenAIEmbeddings(
azure_deployment=config["embedding_model"],
api_version=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION", "2024-02-01"),
)
elif provider == LLMProvider.OLLAMA:
return OllamaEmbeddings(
model=config["embedding_model"],
base_url="http://localhost:11434",
)
def get_mlflow_model_uri(provider: LLMProvider) -> str:
"""Get MLflow model URI for RAGAS scorers (uses litellm format)."""
config = MODEL_CONFIG[provider]
if provider == LLMProvider.OPENAI:
return f"openai:/{config['chat_model']}"
elif provider == LLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI:
# Azure format: azure/<deployment_name>
return f"azure:/{config['chat_model']}"
elif provider == LLMProvider.OLLAMA:
# Ollama format for litellm: ollama/<model_name>
# Note: ollama_chat format has issues with litellm, use ollama/ prefix
return f"ollama:/{config['chat_model']}"
llm = get_llm(PROVIDER)
embeddings = get_embeddings(PROVIDER)
mlflow_model_uri = get_mlflow_model_uri(PROVIDER)
print(f"LLM initialized: {type(llm).__name__}")
print(f"Embeddings initialized: {type(embeddings).__name__}")
print(f"MLflow model URI: {mlflow_model_uri}")
LLM initialized: AzureChatOpenAI Embeddings initialized: AzureOpenAIEmbeddings MLflow model URI: azure:/gpt-4o-mini
Sample Knowledge Base
We'll create a small knowledge base about MLflow - fitting for a tutorial that uses MLflow for evaluation! This dataset contains key concepts that our RAG system will retrieve from.
import json
# Load knowledge base from external file
with open("data/knowledge_base.json") as f:
KNOWLEDGE_BASE = json.load(f)
print(f"Knowledge base contains {len(KNOWLEDGE_BASE)} documents")
for i, doc in enumerate(KNOWLEDGE_BASE, 1):
preview = doc[:80].replace('\n', ' ')
print(f" {i}. {preview}...")
Knowledge base contains 20 documents 1. MLflow Tracking is an API and UI for logging parameters, code versions, metrics,... 2. The MLflow Model Registry is a centralized model store that provides model linea... 3. MLflow GenAI provides specialized tools for developing and evaluating generative... 4. RAGAS (Retrieval Augmented Generation Assessment) is an evaluation framework int... 5. MLflow Projects package code in a reusable, reproducible form. A project is simp... 6. MLflow's autolog feature automatically logs metrics, parameters, and models duri... 7. The MLflow Model format is a standard format for packaging machine learning mode... 8. Evaluation in MLflow can be performed using mlflow.evaluate() for traditional ML... 9. MLflow Model Serving enables deploying models as REST API endpoints. You can ser... 10. MLflow Recipes (formerly MLflow Pipelines) provide predefined templates for comm... 11. The MLflow CLI provides commands for running projects, serving models, and manag... 12. MLflow's REST API allows programmatic access to the tracking server. Endpoints i... 13. MLflow experiments organize runs into logical groups. Each experiment has a uniq... 14. MLflow provides run comparison capabilities through the UI and API. The Compare ... 15. MLflow artifacts are files associated with runs, such as models, data files, and... 16. Model signatures in MLflow define the expected input and output schema for model... 17. MLflow on Databricks provides managed MLflow tracking, model registry, and model... 18. MLflow supports multiple environment managers for reproducibility. Projects can ... 19. MLflow Prompt Engineering tools help develop and version prompts for LLM applica... 20. MLflow integrates with LangChain through mlflow.langchain module. The integratio...
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_core.documents import Document
documents = [Document(page_content=doc.strip()) for doc in KNOWLEDGE_BASE]
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=500,
chunk_overlap=50,
)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
print(f"Split into {len(splits)} chunks")
Split into 20 chunks
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(splits, embeddings)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
print(f"Vector store created with {vectorstore.index.ntotal} vectors")
Vector store created with 20 vectors
test_query = "What metrics does RAGAS provide?"
test_results = retriever.invoke(test_query)
print(f"Test query: '{test_query}'")
print(f"Retrieved {len(test_results)} documents:")
for i, doc in enumerate(test_results, 1):
print(f"\n--- Document {i} ---")
print(doc.page_content[:200] + "...")
Test query: 'What metrics does RAGAS provide?' Retrieved 3 documents: --- Document 1 --- RAGAS (Retrieval Augmented Generation Assessment) is an evaluation framework integrated with MLflow for assessing RAG pipelines. Key metrics include: Faithfulness (measures if the answer is grounded i... --- Document 2 --- MLflow GenAI provides specialized tools for developing and evaluating generative AI applications. It includes mlflow.genai.evaluate() for systematic assessment of LLM outputs using configurable scorer... --- Document 3 --- Evaluation in MLflow can be performed using mlflow.evaluate() for traditional ML models or mlflow.genai.evaluate() for generative AI applications. For GenAI, evaluation uses Scorer objects that can be...
Minimal RAG Pipeline
We'll build a simple RAG chain using LangChain's LCEL (LangChain Expression Language) that:
- Retrieves relevant context from our FAISS vector store
- Formats a prompt with the context and question
- Generates an answer using the LLM
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
RAG_PROMPT = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""
You are a helpful assistant answering questions about MLflow.
Use ONLY the following context to answer the question.
If the context doesn't contain the answer, say "I don't have enough information to answer this question."
Context:
{context}
Question: {question}
Answer:
""")
def format_docs(docs):
return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
rag_chain = (
{
"context": retriever | format_docs,
"question": RunnablePassthrough(),
}
| RAG_PROMPT
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
print("RAG chain created successfully")
RAG chain created successfully
test_answer = rag_chain.invoke("What is MLflow Tracking?")
print("Test Question: What is MLflow Tracking?")
print(f"\nAnswer: {test_answer}")
Test Question: What is MLflow Tracking? Answer: MLflow Tracking is an API and UI for logging parameters, code versions, metrics, and artifacts when running your machine learning code. It allows you to log and query experiments using Python, REST, R API, and Java API. The MLflow Tracking component lets you log source code, models, and visualizations. Each run records: code version, start and end time, source, parameters, metrics, and artifacts.
Enable MLflow Tracing
MLflow's LangChain integration can automatically capture traces of our RAG pipeline invocations. This is essential for evaluation - RAGAS scorers analyze these traces to compute metrics.
import mlflow
mlflow.set_experiment("RAG-Evaluation-Tutorial")
mlflow.langchain.autolog(log_traces=True)
print(f"MLflow experiment: {mlflow.get_experiment_by_name('RAG-Evaluation-Tutorial').name}")
print("LangChain autologging enabled with tracing")
2026/01/11 09:22:25 INFO mlflow.store.db.utils: Creating initial MLflow database tables... 2026/01/11 09:22:25 INFO mlflow.store.db.utils: Updating database tables 2026/01/11 09:22:25 INFO alembic.runtime.migration: Context impl SQLiteImpl. 2026/01/11 09:22:25 INFO alembic.runtime.migration: Will assume non-transactional DDL. 2026/01/11 09:22:25 INFO alembic.runtime.migration: Context impl SQLiteImpl. 2026/01/11 09:22:25 INFO alembic.runtime.migration: Will assume non-transactional DDL.
MLflow experiment: RAG-Evaluation-Tutorial LangChain autologging enabled with tracing
NOTE: If you don't have tracing enabled in your RAG there is still possibility to pass the evaluation data to MLflow to ease analysis. If this is your case please refer to the text on my blog explaining how to do it: RAG Evaluation with RAGAS and MLflow - without tracing
Load Golden Dataset
A golden dataset (also called ground truth or evaluation dataset) contains:
- Questions: User queries we want to evaluate
- Expected Answers: The correct/ideal responses
- Expected Contexts (optional): Which documents should be retrieved
This dataset allows us to systematically measure our RAG system's quality.
# Load golden dataset from external file
with open("data/golden_dataset.json") as f:
GOLDEN_DATASET = json.load(f)
eval_df = pd.DataFrame(GOLDEN_DATASET)
print(f"Golden dataset contains {len(GOLDEN_DATASET)} evaluation samples")
eval_df.head(2)
Golden dataset contains 20 evaluation samples
| question | ground_truth | contexts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | What is MLflow Tracking used for? | MLflow Tracking is used for logging parameters... | [MLflow Tracking is an API and UI for logging ... |
| 1 | What features does the MLflow Model Registry p... | The MLflow Model Registry provides model linea... | [The MLflow Model Registry is a centralized mo... |
Generate RAG Responses for Evaluation
We'll run our RAG pipeline on each question and collect the responses along with the retrieved contexts. This data will be used by RAGAS scorers.
# Define traced RAG function for evaluation
# IMPORTANT: Function parameter names must match keys in data['inputs']
# Since inputs={'question': ...}, the function must accept 'question' parameter
@mlflow.trace(span_type="CHAIN")
def traced_rag_predict(question: str) -> dict:
"""Traced RAG prediction function for mlflow.genai.evaluate().
Args:
question: The question to answer (matches inputs['question'] key)
Returns:
dict with 'response' and 'retrieved_contexts' for RAGAS scorers
"""
# Retrieval step - creates RETRIEVER span
with mlflow.start_span(name="retriever", span_type="RETRIEVER") as span:
retrieved_docs = retriever.invoke(question)
contexts = [doc.page_content for doc in retrieved_docs]
span.set_inputs({"question": question})
span.set_outputs({"retrieved_contexts": contexts})
# Generation step - creates LLM span
with mlflow.start_span(name="generator", span_type="LLM") as span:
answer = rag_chain.invoke(question)
span.set_inputs({"question": question, "contexts": contexts})
span.set_outputs({"response": answer})
return {
"response": answer,
"retrieved_contexts": contexts,
}
# Preview a sample from the golden dataset
# Note: With predict_fn approach, answers are generated during evaluation
sample_idx = 2
print(f"Sample evaluation record #{sample_idx + 1}:")
print(f"\nQuestion: {eval_df.iloc[sample_idx]['question']}")
print(f"\nExpected Answer: {eval_df.iloc[sample_idx]['ground_truth']}")
# Show what the traced function would produce for this question
print(f"\n--- Testing RAG response for this question ---")
test_output = traced_rag_predict(question=eval_df.iloc[sample_idx]['question'])
print(f"\nRAG Answer: {test_output['response']}")
print(f"\nRetrieved Contexts ({len(test_output['retrieved_contexts'])}):\n")
for j, ctx in enumerate(test_output['retrieved_contexts'], 1):
print(f" Context {j}: {ctx[:100]}...\n")
Sample evaluation record #3: Question: What metrics does RAGAS provide for RAG evaluation? Expected Answer: RAGAS provides four key metrics: Faithfulness (measures if the answer is grounded in context), Context Precision (evaluates if relevant documents are ranked higher), Context Recall (checks if context contains all needed information), and Factual Correctness (compares output against expected answers). --- Testing RAG response for this question --- RAG Answer: RAGAS provides the following key metrics for RAG evaluation: Faithfulness, Context Precision, Context Recall, and Factual Correctness. Retrieved Contexts (3): Context 1: RAGAS (Retrieval Augmented Generation Assessment) is an evaluation framework integrated with MLflow ... Context 2: Evaluation in MLflow can be performed using mlflow.evaluate() for traditional ML models or mlflow.ge... Context 3: MLflow GenAI provides specialized tools for developing and evaluating generative AI applications. It...
RAGAS Evaluation with MLflow
Now we'll use MLflow's RAGAS integration to evaluate our RAG pipeline. The key metrics we'll compute:
| Metric | What it measures | Required Data | Common Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faithfulness | Is the answer grounded in retrieved context? | answer, contexts | Missing RETRIEVER spans |
| Context Precision | Are relevant docs ranked higher? | question, contexts, ground_truth | No ground_truth provided |
| Context Recall | Does context contain needed info? | contexts, ground_truth | No ground_truth provided |
| Factual Correctness | Does answer match expected? | answer, ground_truth | Semantic mismatch (strict) |
These metrics provide an initial quantitative assessment of RAG quality across multiple dimensions. There are more RAGAS tool metrics available through the MLflow integration.
Note on LLM Judge: RAGAS metrics use an LLM as a judge. For best results, use OpenAI (gpt-4o-mini) as the judge model even if you're using Ollama for RAG generation. Ollama/local models may have issues with litellm's structured output parsing. Set
JUDGE_PROVIDER = LLMProvider.OPENAIbelow if you encounter scoring errors with Ollama.
# Test litellm connectivity (optional - helps debug scoring issues)
import litellm
def test_litellm_connection(model_uri: str) -> bool:
"""Test if litellm can connect to the model."""
try:
response = litellm.completion(
model=model_uri,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Say 'test' and nothing else."}],
max_tokens=10,
)
print(f"✓ litellm connection successful: {model_uri}")
print(f" Response: {response.choices[0].message.content[:50]}...")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"✗ litellm connection failed: {model_uri}")
print(f" Error: {type(e).__name__}: {str(e)[:100]}")
return False
# Test the judge model connection
judge_model_uri = get_mlflow_model_uri(PROVIDER)
print(f"Testing judge model: {judge_model_uri}\n")
litellm_ok = test_litellm_connection(judge_model_uri)
if not litellm_ok:
print("\n⚠️ Consider using OpenAI as judge model for reliable scoring.")
print(" Set JUDGE_PROVIDER = LLMProvider.OPENAI in the next cell.")
Testing judge model: azure:/gpt-4o-mini Provider List: https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers Provider List: https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers ✗ litellm connection failed: azure:/gpt-4o-mini Error: BadRequestError: litellm.BadRequestError: LLM Provider NOT provided. Pass in the LLM provider you are trying to call. ⚠️ Consider using OpenAI as judge model for reliable scoring. Set JUDGE_PROVIDER = LLMProvider.OPENAI in the next cell.
from mlflow.genai.scorers.ragas import (
Faithfulness,
ContextPrecision,
ContextRecall,
FactualCorrectness,
)
# Configure the judge model for RAGAS evaluation
# For reliable scoring, use OpenAI even when using Ollama for RAG generation
JUDGE_PROVIDER = PROVIDER # Change to LLMProvider.OPENAI for better results
judge_model_uri = get_mlflow_model_uri(JUDGE_PROVIDER)
print(f"Judge model: {judge_model_uri}")
print(f"(Change JUDGE_PROVIDER to LLMProvider.OPENAI if scoring fails with Ollama)\n")
# Note: ContextPrecision and ContextRecall require traces with RETRIEVER spans
# For evaluation without traces, use Faithfulness and FactualCorrectness
scorers = [
Faithfulness(model=judge_model_uri),
FactualCorrectness(model=judge_model_uri),
# These require traces with retriever spans - may show errors without proper tracing:
ContextPrecision(model=judge_model_uri),
ContextRecall(model=judge_model_uri),
]
print(f"Configured {len(scorers)} RAGAS scorers:")
for scorer in scorers:
print(f" - {type(scorer).__name__}")
Judge model: azure:/gpt-4o-mini (Change JUDGE_PROVIDER to LLMProvider.OPENAI if scoring fails with Ollama) Configured 4 RAGAS scorers: - Faithfulness - FactualCorrectness - ContextPrecision - ContextRecall
Prepare Evaluation Data
MLflow's genai.evaluate() expects data in a specific format. We need to map our data to the expected schema.
# Prepare evaluation data for predict_fn approach
# With predict_fn, we pass inputs and expectations - outputs come from the traced function
eval_data = []
for _, row in eval_df.iterrows():
eval_data.append({
"inputs": {"question": row["question"]},
"expectations": {
"ground_truth": row["ground_truth"],
"contexts": row.get("contexts", []), # For ContextRecall
},
})
print(f"Prepared {len(eval_data)} samples for evaluation")
print(f"\nSample format:")
print(f" inputs: {list(eval_data[0]['inputs'].keys())}")
print(f" expectations: {list(eval_data[0]['expectations'].keys())}")
if eval_data[0]['expectations'].get('ground_truth'):
print(f" ground_truth contexts: {len(eval_data[0]['expectations']['ground_truth'])} items")
print(f"\nNote: outputs will be generated by traced_rag_predict() during evaluation")
print(f" ground_truth enables ContextPrecision and ContextRecall metrics")
Prepared 20 samples for evaluation
Sample format:
inputs: ['question']
expectations: ['ground_truth', 'contexts']
ground_truth contexts: 205 items
Note: outputs will be generated by traced_rag_predict() during evaluation
ground_truth enables ContextPrecision and ContextRecall metrics
print("Running RAGAS evaluation with traced predict_fn...")
print("This generates traces with RETRIEVER spans for Faithfulness metric.\n")
with mlflow.start_run(run_name="ragas-evaluation-traced") as run:
mlflow.log_param("provider", PROVIDER.value)
mlflow.log_param("model", MODEL_CONFIG[PROVIDER]["chat_model"])
mlflow.log_param("num_samples", len(eval_data))
mlflow.log_param("retriever_k", 3)
mlflow.log_param("evaluation_mode", "predict_fn")
# Use predict_fn to generate traces with RETRIEVER spans
# This allows Faithfulness scorer to access retrieved_contexts
eval_results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
predict_fn=traced_rag_predict,
data=eval_data,
scorers=scorers,
)
run_id = run.info.run_id
print(f"\nEvaluation complete! Run ID: {run_id}")
2026/01/11 09:22:33 INFO mlflow.models.evaluation.utils.trace: Auto tracing is temporarily enabled during the model evaluation for computing some metrics and debugging. To disable tracing, call `mlflow.autolog(disable=True)`. 2026/01/11 09:22:33 INFO mlflow.genai.utils.data_validation: Testing model prediction with the first sample in the dataset. To disable this check, set the MLFLOW_GENAI_EVAL_SKIP_TRACE_VALIDATION environment variable to True. 2026/01/11 09:22:33 WARNING mlflow.tracing.fluent: Failed to start span VectorStoreRetriever: 'NonRecordingSpan' object has no attribute 'context'. For full traceback, set logging level to debug.
Running RAGAS evaluation with traced predict_fn... This generates traces with RETRIEVER spans for Faithfulness metric.
2026/01/11 09:22:34 WARNING mlflow.tracing.fluent: Failed to start span RunnableSequence: 'NonRecordingSpan' object has no attribute 'context'. For full traceback, set logging level to debug.
Evaluating: 0%| | 0/20 [Elapsed: 00:00, Remaining: ?]
✨ Evaluation completed. Metrics and evaluation results are logged to the MLflow run: Run name: ragas-evaluation-traced Run ID: 35029b87d0e542128dedd53531ba0710 To view the detailed evaluation results with sample-wise scores, open the Traces tab in the Run page in the MLflow UI. Evaluation complete! Run ID: 35029b87d0e542128dedd53531ba0710
MLflow Results Analysis
Let's examine the evaluation results both programmatically and understand how to view them in the MLflow UI.
print("=" * 60)
print("RAGAS EVALUATION RESULTS")
print("=" * 60)
results_df = eval_results.tables["eval_results"]
# Find RAGAS scorer columns (Faithfulness, FactualCorrectness, Context*)
import pandas as pd
ragas_metrics = ['Faithfulness', 'FactualCorrectness', 'ContextPrecision', 'ContextRecall']
value_columns = [col for col in results_df.columns
if col.endswith('/value') and any(m in col for m in ragas_metrics)]
error_columns = [col for col in results_df.columns
if col.endswith('/error') and any(m in col for m in ragas_metrics)]
print("\nRAGAS Metrics:")
print("-" * 40)
successful_metrics = 0
failed_metrics = 0
for col in value_columns:
# Convert to numeric, coercing errors to NaN
numeric_col = pd.to_numeric(results_df[col], errors='coerce')
non_null = numeric_col.dropna()
total = len(results_df)
success_count = len(non_null)
if success_count > 0:
mean_val = non_null.mean()
std_val = non_null.std() if len(non_null) > 1 else 0
print(f" ✓ {col}: {mean_val:.3f} (±{std_val:.3f}) [{success_count}/{total} samples]")
successful_metrics += 1
else:
print(f" ✗ {col}: NO SCORES (0/{total} samples succeeded)")
failed_metrics += 1
print(f"\nSummary: {successful_metrics} metrics succeeded, {failed_metrics} metrics failed")
print(f" Total samples: {len(results_df)}")
# Error diagnostics (if any metrics failed)
if failed_metrics > 0:
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("🔍 DIAGNOSTIC: Error Details for Failed Metrics")
print("=" * 60)
for col in error_columns:
metric_name = col.replace('/error', '')
errors = results_df[col].dropna()
if len(errors) > 0:
print(f"\n❌ {metric_name}:")
# Get first unique error message
unique_errors = errors.unique()
for err in unique_errors[:2]: # Show max 2 unique errors
# Truncate long error messages
err_str = str(err)[:300]
if len(str(err)) > 300:
err_str += "..."
print(f" {err_str}")
print("\n" + "-" * 60)
print("Common fixes:")
print(" 1. Use OpenAI as judge: JUDGE_PROVIDER = LLMProvider.OPENAI")
print(" 2. For Ollama: ensure model is running and OLLAMA_API_BASE is set")
print(" 3. ContextPrecision/ContextRecall require traces with RETRIEVER spans")
else:
print("\n✅ All metrics computed successfully!")
============================================================ RAGAS EVALUATION RESULTS ============================================================ RAGAS Metrics: ---------------------------------------- ✓ ContextRecall/value: 0.853 (±0.196) [20/20 samples] ✓ ContextPrecision/value: 0.967 (±0.116) [20/20 samples] ✓ Faithfulness/value: 0.984 (±0.047) [20/20 samples] ✓ FactualCorrectness/value: 0.613 (±0.250) [20/20 samples] Summary: 4 metrics succeeded, 0 metrics failed Total samples: 20 ✅ All metrics computed successfully!
# Helper function to extract question from request column
def extract_question(request_data):
"""Extract question from MLflow request column."""
if isinstance(request_data, dict):
return str(request_data.get("question", "N/A"))[:60]
elif isinstance(request_data, str):
return request_data[:60]
return "N/A"
# Display results summary with metric columns
available_cols = [col for col in value_columns if col in results_df.columns]
results_summary = results_df[available_cols].copy()
# Add question column from request data
if "request" in results_df.columns:
results_summary.insert(0, "question", results_df["request"].apply(extract_question))
results_summary
print("\nIdentifying Low-Scoring Samples:")
print("-" * 40)
for col in value_columns:
if col in results_df.columns:
numeric_col = pd.to_numeric(results_df[col], errors='coerce')
low_mask = numeric_col < 0.5
low_scores = results_df[low_mask]
if len(low_scores) > 0:
print(f"\n⚠️ {col} < 0.5: {len(low_scores)} samples")
for idx, row in low_scores.iterrows():
question = extract_question(row.get("request", {}))
score = numeric_col.loc[idx]
if pd.notna(score):
print(f" - [{score:.2f}] {question}...")
Identifying Low-Scoring Samples:
----------------------------------------
⚠️ ContextRecall/value < 0.5: 1 samples
- [0.33] What is MLflow GenAI used for?...
⚠️ ContextPrecision/value < 0.5: 1 samples
- [0.50] How can you run MLflow Projects?...
⚠️ FactualCorrectness/value < 0.5: 6 samples
- [0.46] What is MLflow Tracking used for?...
- [0.30] What is MLflow GenAI used for?...
- [0.47] How can you run MLflow Projects?...
- [0.12] What is Faithfulness in RAGAS?...
- [0.31] What frameworks support MLflow autolog?...
- [0.40] How can you access MLflow programmatically via REST API?...
Interpreting RAGAS Scores
All RAGAS metrics return scores between 0.0 and 1.0. Here's rough guidance:
| Score Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 0.9 - 1.0 | Excellent - production ready |
| 0.7 - 0.9 | Good - minor improvements needed |
| 0.5 - 0.7 | Fair - significant room for improvement |
| < 0.5 | Poor - investigate specific failures |
Important caveats:
- These thresholds are guidelines, not absolutes
- Different applications have different quality requirements
- Low FactualCorrectness often reflects semantic similarity issues, not actual incorrectness
- Focus on relative improvements when comparing variants, not absolute scores
To view detailed results in the MLflow UI:
Start MLflow UI (if not running):
$ mlflow ui --port 5000Open http://localhost:5000 in your browser
Navigate to:
- Experiment: 'RAG-Evaluation-Tutorial'
- Run: 'ragas-evaluation'
In the run details, you'll find:
- Parameters: model configuration
- Metrics: aggregate RAGAS scores
- Artifacts: detailed evaluation tables
- Traces: individual RAG invocations
print(f"Run ID: {run_id}")
Run ID: 35029b87d0e542128dedd53531ba0710
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("🎉 Tutorial Complete!")
print("=" * 60)
print(f"""
Summary:
- Provider: {PROVIDER.value}
- Model: {MODEL_CONFIG[PROVIDER]['chat_model']}
- Samples evaluated: {len(eval_data)}
- MLflow Run ID: {run_id}
View results: mlflow ui --port 5000
""")
============================================================ 🎉 Tutorial Complete! ============================================================ Summary: - Provider: azure_openai - Model: gpt-4o-mini - Samples evaluated: 20 - MLflow Run ID: 35029b87d0e542128dedd53531ba0710 View results: mlflow ui --port 5000
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
During development of this tutorial, several non-obvious issues emerged:
Model URI Format
MLflow uses litellm under the hood. The URI format matters:
- OpenAI:
openai:/gpt-4o-mini(note the colon-slash) - Azure:
azure:/deployment-name - Ollama:
ollama:/llama3.2:3b
Using azure/ instead of azure:/ will fail silently or produce cryptic errors.
Function Signature Must Match Input Keys
When using predict_fn, the function parameter names must exactly match the keys in your inputs dictionary:
# If your data has: {"inputs": {"question": "..."}}
# Your function MUST be: def predict(question: str) # NOT def predict(query: str)
RETRIEVER Spans for Context Metrics
Faithfulness, ContextPrecision, and ContextRecall require traces with RETRIEVER-type spans. Without them, these metrics return errors or incorrect values. The traced_rag_predict function in this tutorial creates these spans explicitly.
Judge Model Limitations
RAGAS metrics use an LLM as a judge. Local models (Ollama) may struggle with the structured output parsing that RAGAS requires. For reliable scoring, consider using OpenAI/Azure as the judge even when your RAG uses a different provider.
Extras: Comparing RAG Variants with MLflow
One of MLflow's key strengths is enabling systematic A/B comparisons between different RAG configurations. Here's how to structure experiments comparing variants like chunk sizes, models, or retrieval strategies.
Example: Comparing Chunk Sizes
# Comparing RAG Variants: Different Chunk Sizes
# This demonstrates how to evaluate the same RAG pipeline with different configurations
print("Running chunk size comparison experiments...")
print("=" * 60)
CHUNK_SIZES = [50, 150]
experiment_run_ids = []
for chunk_size in CHUNK_SIZES:
print(f"\nTesting chunk_size={chunk_size}")
# Rebuild the vector store with new chunk size
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=chunk_size,
chunk_overlap=chunk_size // 10
)
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# Update the global vectorstore and retriever used by traced_rag_predict
global vectorstore, retriever
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, embeddings)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
print(f" Created {len(chunks)} chunks")
# Run evaluation
with mlflow.start_run(run_name=f"chunk-size-{chunk_size}") as run:
mlflow.log_param("chunk_size", chunk_size)
mlflow.log_param("chunk_overlap", chunk_size // 10)
mlflow.log_param("num_chunks", len(chunks))
eval_results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
predict_fn=traced_rag_predict,
data=eval_data,
scorers=scorers,
)
experiment_run_ids.append(run.info.run_id)
print(f" ✓ Run ID: {run.info.run_id}")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print(f"Completed {len(CHUNK_SIZES)} experiments. Run IDs saved for comparison.")
Running chunk size comparison experiments... ============================================================ Testing chunk_size=50
2026/01/11 09:23:10 INFO mlflow.genai.utils.data_validation: Testing model prediction with the first sample in the dataset. To disable this check, set the MLFLOW_GENAI_EVAL_SKIP_TRACE_VALIDATION environment variable to True. 2026/01/11 09:23:10 WARNING mlflow.tracing.fluent: Failed to start span VectorStoreRetriever: 'NonRecordingSpan' object has no attribute 'context'. For full traceback, set logging level to debug. 2026/01/11 09:23:10 WARNING mlflow.tracing.fluent: Failed to start span RunnableSequence: 'NonRecordingSpan' object has no attribute 'context'. For full traceback, set logging level to debug.
Created 175 chunks
Evaluating: 0%| | 0/20 [Elapsed: 00:00, Remaining: ?]
✨ Evaluation completed. Metrics and evaluation results are logged to the MLflow run: Run name: chunk-size-50 Run ID: 34464d4c3bb34a0a8ce4d43760149f1e To view the detailed evaluation results with sample-wise scores, open the Traces tab in the Run page in the MLflow UI. ✓ Run ID: 34464d4c3bb34a0a8ce4d43760149f1e Testing chunk_size=150
2026/01/11 09:23:33 INFO mlflow.genai.utils.data_validation: Testing model prediction with the first sample in the dataset. To disable this check, set the MLFLOW_GENAI_EVAL_SKIP_TRACE_VALIDATION environment variable to True. 2026/01/11 09:23:33 WARNING mlflow.tracing.fluent: Failed to start span VectorStoreRetriever: 'NonRecordingSpan' object has no attribute 'context'. For full traceback, set logging level to debug. 2026/01/11 09:23:33 WARNING mlflow.tracing.fluent: Failed to start span RunnableSequence: 'NonRecordingSpan' object has no attribute 'context'. For full traceback, set logging level to debug.
Created 62 chunks
Evaluating: 0%| | 0/20 [Elapsed: 00:00, Remaining: ?]
✨ Evaluation completed. Metrics and evaluation results are logged to the MLflow run: Run name: chunk-size-150 Run ID: c77546d4d930426b98ebeb1bf1a09a3f To view the detailed evaluation results with sample-wise scores, open the Traces tab in the Run page in the MLflow UI. ✓ Run ID: c77546d4d930426b98ebeb1bf1a09a3f ============================================================ Completed 2 experiments. Run IDs saved for comparison.
Comparing Results in MLflow UI
After running multiple variants:
- Open MLflow UI:
mlflow ui --port 5000 - Navigate to your experiment
- Select runs to compare using checkboxes
- Click Compare to see side-by-side metrics
- Use Chart view to visualize metric differences
You can also compare programmatically:
# Compare Results Programmatically
# Query MLflow for runs and display a formatted comparison table
experiment_name = "RAG-Evaluation-Tutorial"
# Get runs with chunk_size parameter (our comparison experiments)
runs_df = mlflow.search_runs(
experiment_names=[experiment_name],
filter_string="params.chunk_size != ''",
order_by=["params.chunk_size ASC"]
)
if len(runs_df) == 0:
print("No chunk size comparison runs found. Run the comparison cell above first.")
else:
# Debug: show available metric columns
metric_cols = [c for c in runs_df.columns if c.startswith("metrics.")]
print(f"Available metric columns ({len(metric_cols)} total):")
for col in metric_cols[:8]: # Show first 8
print(f" - {col}")
# Define metrics we want (will search for partial matches)
metric_names = ["Faithfulness", "FactualCorrectness", "ContextPrecision", "ContextRecall"]
# Find actual column names (may have backticks or different format)
def find_metric_col(df, metric_name):
"""Find column containing metric_name in its name."""
for col in df.columns:
if metric_name in col and "mean" in col:
return col
return None
comparison_data = []
for _, run in runs_df.iterrows():
row = {
"Run Name": run.get("tags.mlflow.runName", "N/A"),
"Chunk Size": run.get("params.chunk_size", "N/A"),
"Num Chunks": run.get("params.num_chunks", "N/A"),
}
for metric_name in metric_names:
col = find_metric_col(runs_df, metric_name)
if col:
value = run.get(col)
row[metric_name] = f"{value:.3f}" if pd.notna(value) else "N/A"
else:
row[metric_name] = "N/A"
comparison_data.append(row)
comparison_df = pd.DataFrame(comparison_data)
print("\nChunk Size Comparison Results")
print("=" * 80)
print(comparison_df.to_string(index=False))
# Find best configuration
if "FactualCorrectness" in comparison_df.columns:
best_idx = comparison_df["FactualCorrectness"].apply(
lambda x: float(x) if x != "N/A" else 0
).idxmax()
print(f"\n✨ Best configuration: {comparison_df.iloc[best_idx]['Run Name']}")
Available metric columns (4 total):
- metrics.Faithfulness/mean
- metrics.FactualCorrectness/mean
- metrics.ContextRecall/mean
- metrics.ContextPrecision/mean
Chunk Size Comparison Results
================================================================================
Run Name Chunk Size Num Chunks Faithfulness FactualCorrectness ContextPrecision ContextRecall
chunk-size-150 150 62 0.911 0.768 0.992 0.890
chunk-size-150 150 62 0.915 0.781 0.983 0.834
chunk-size-50 50 175 0.942 0.743 0.983 0.840
chunk-size-50 50 175 0.944 0.758 0.983 0.844
✨ Best configuration: chunk-size-150
How to inspect results in MLflow UI:
Select the experiment to inspect
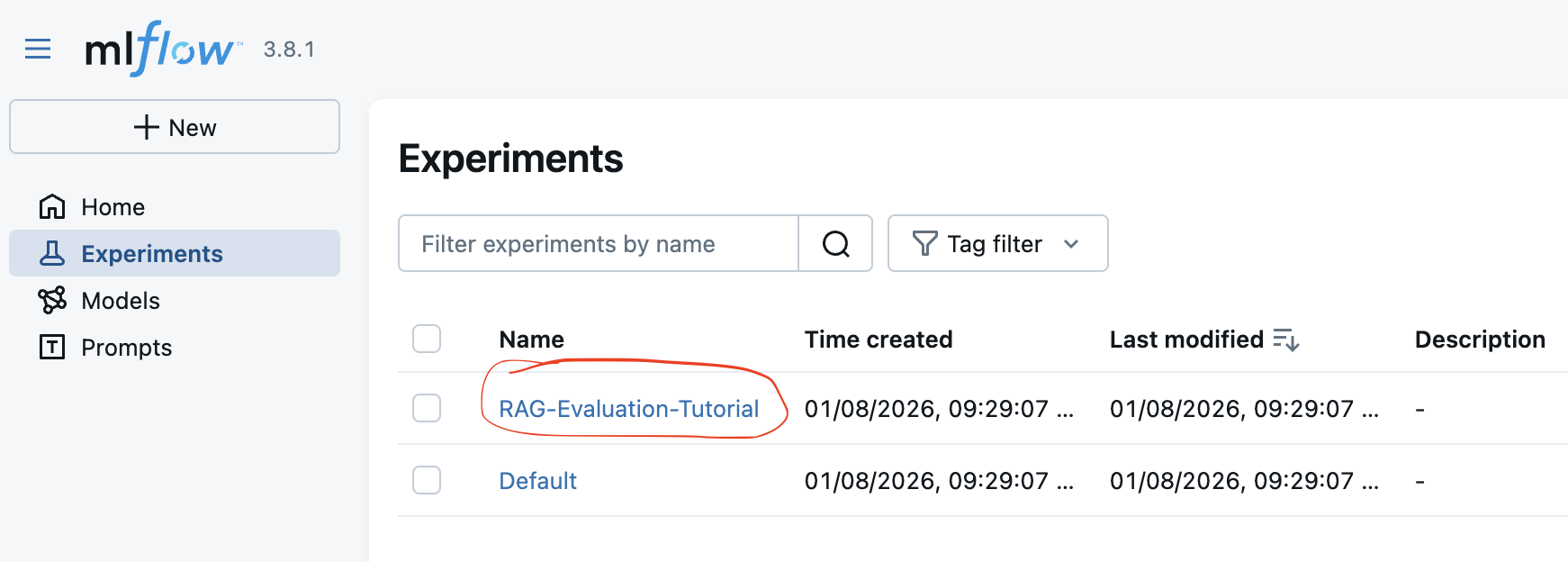 Figure 1: Select the experiment you want to analyze.
Figure 1: Select the experiment you want to analyze.
Experiment type should be automatically recognized as "GenAI Evaluation" - when opening the experiment for the first time - you need to confirm this. Perhaps there is a way to pass this parameter when creating the experiment via code, but I have not found it yet.
Configure comparison of the runs
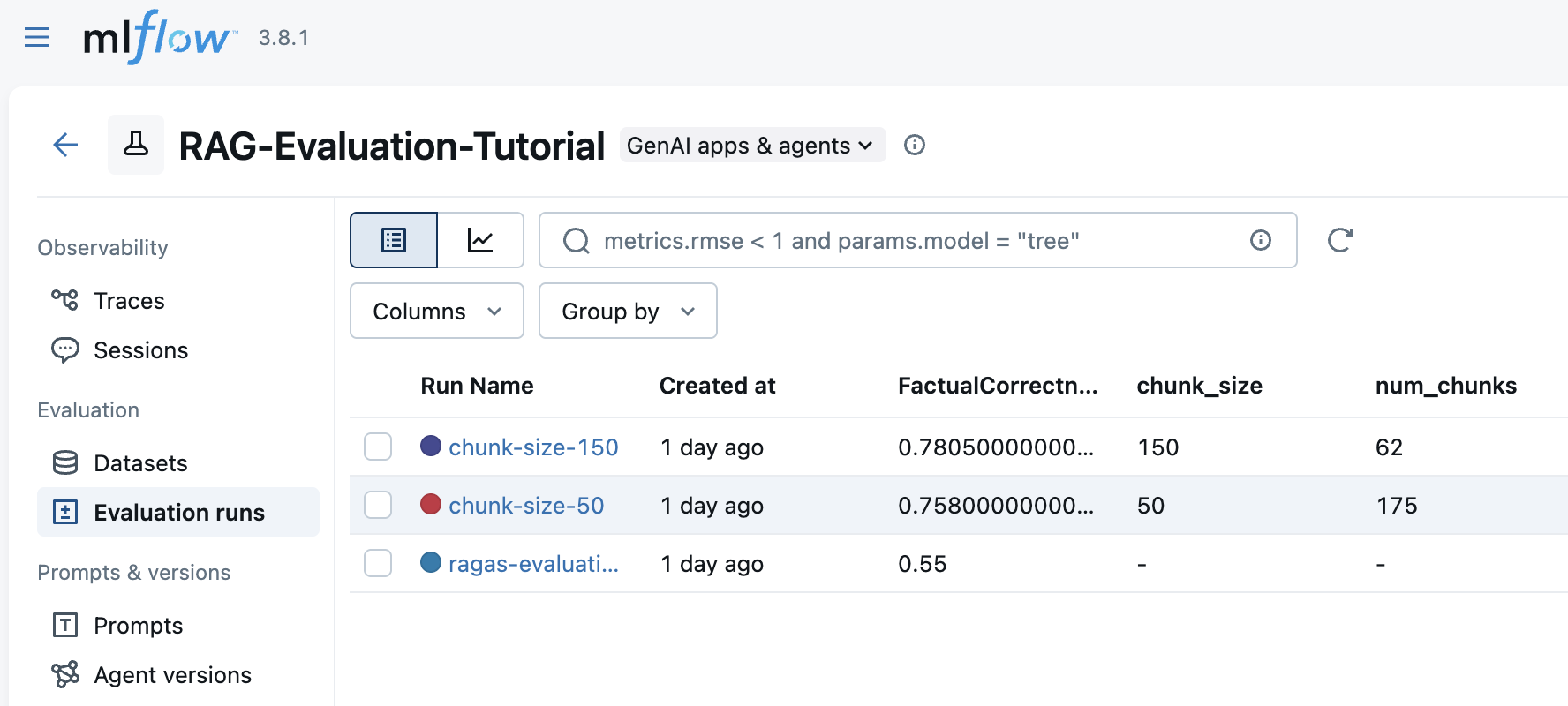 Figure 2: Runs overview - high level overview of the results achieved for the various configurations/variant of your RAG under evaluation.
Figure 2: Runs overview - high level overview of the results achieved for the various configurations/variant of your RAG under evaluation.
- You can edit experiment name and description here. Informative names help when comparing multiple experiments. Description can provide additional context about the experiment's purpose.
NOTE: Perhaps there is a way to pass description when creating the experiment via code, but I have not found it yet.
In this view you can see all the runs (evaluate RAG variants) that belongs to this experiment. Each run corresponds to a different RAG configuration (e.g., different chunk sizes, models, etc.). You can see parameters (e.g., model name, chunk size), aggregated metrics (e.g., mean Faithfulness, mean Context Precision). The displayed columns with parameters, metrics can be customized using the "Columns" button on the top right, so you can focus on the most relevant information.
If you want to do the comparison of two runs, select the runs you want to compare by checking the checkboxes next to each run. Note that, the second run you select will be treated as the "baseline" run in the comparison. The score changes of the first selected run will be calculated against the second selected run.
You can select multiple runs to compare their metrics side-by-side. This is useful for evaluating different RAG configurations.
You can also select columns to display in the comparison table.
View Comparison Results
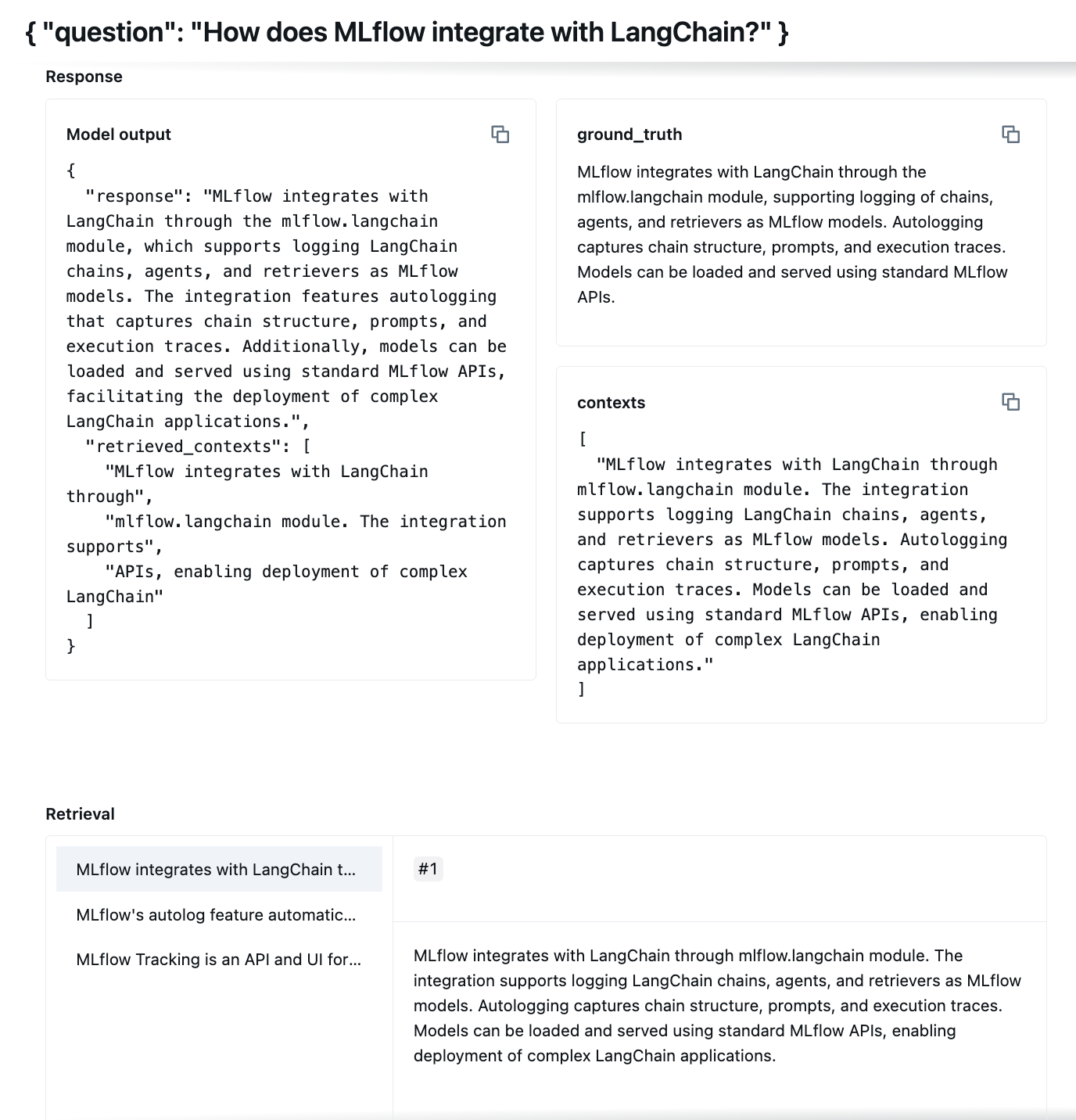 Figure 3: Comparison of individual question results for selected runs.
In this view, you can see detailed comparison of individual question results for the selected runs. The zoom of the single panel is presented in the Figure 4** below. This helps to analyze how each RAG configuration performed on specific queries. You can inspects full RAG output and details like retrieved contexts for each question.
Figure 3: Comparison of individual question results for selected runs.
In this view, you can see detailed comparison of individual question results for the selected runs. The zoom of the single panel is presented in the Figure 4** below. This helps to analyze how each RAG configuration performed on specific queries. You can inspects full RAG output and details like retrieved contexts for each question.
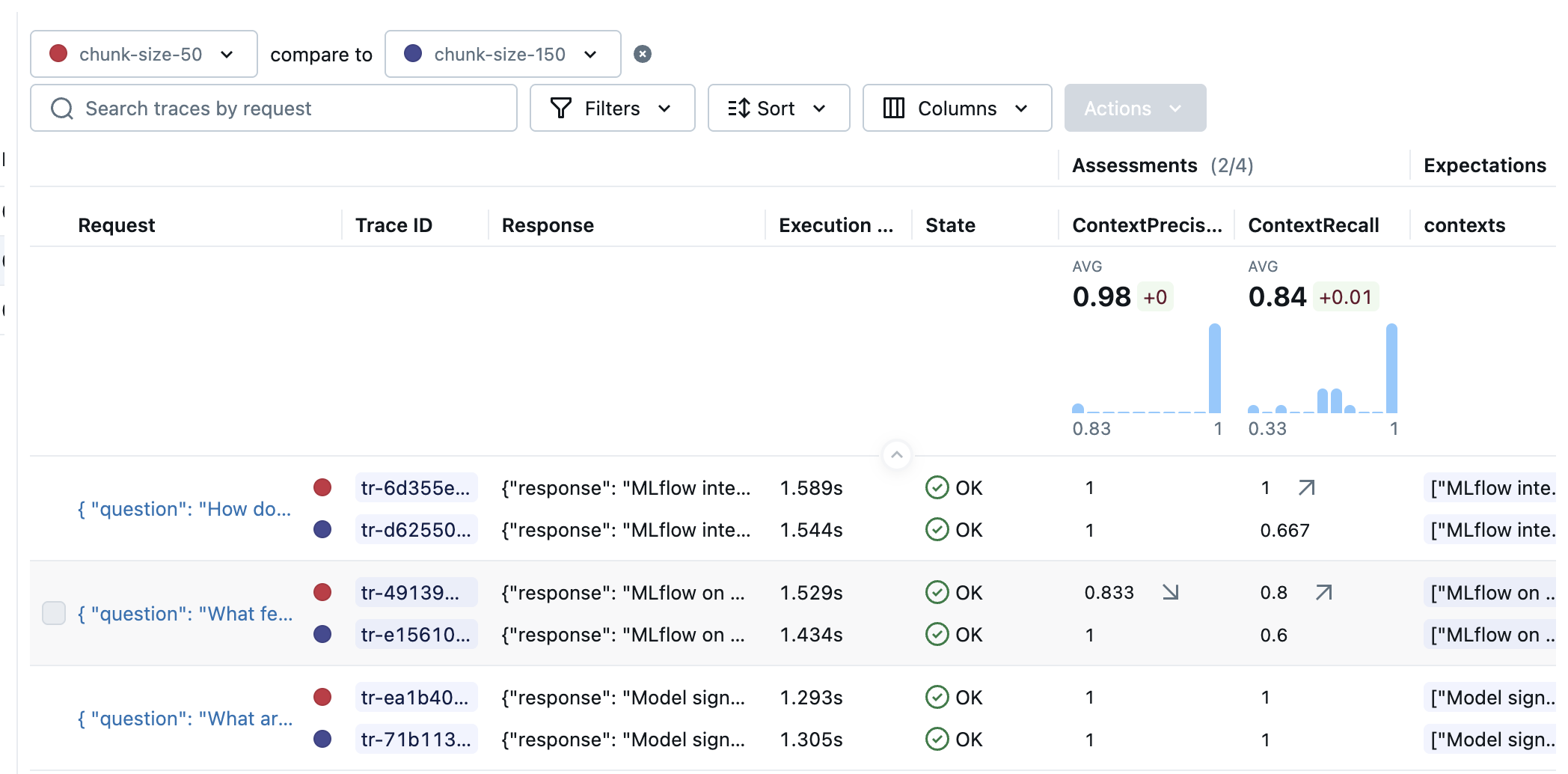 Figure 4: Zoom at the detailed results for the single variant
Figure 4: Zoom at the detailed results for the single variant
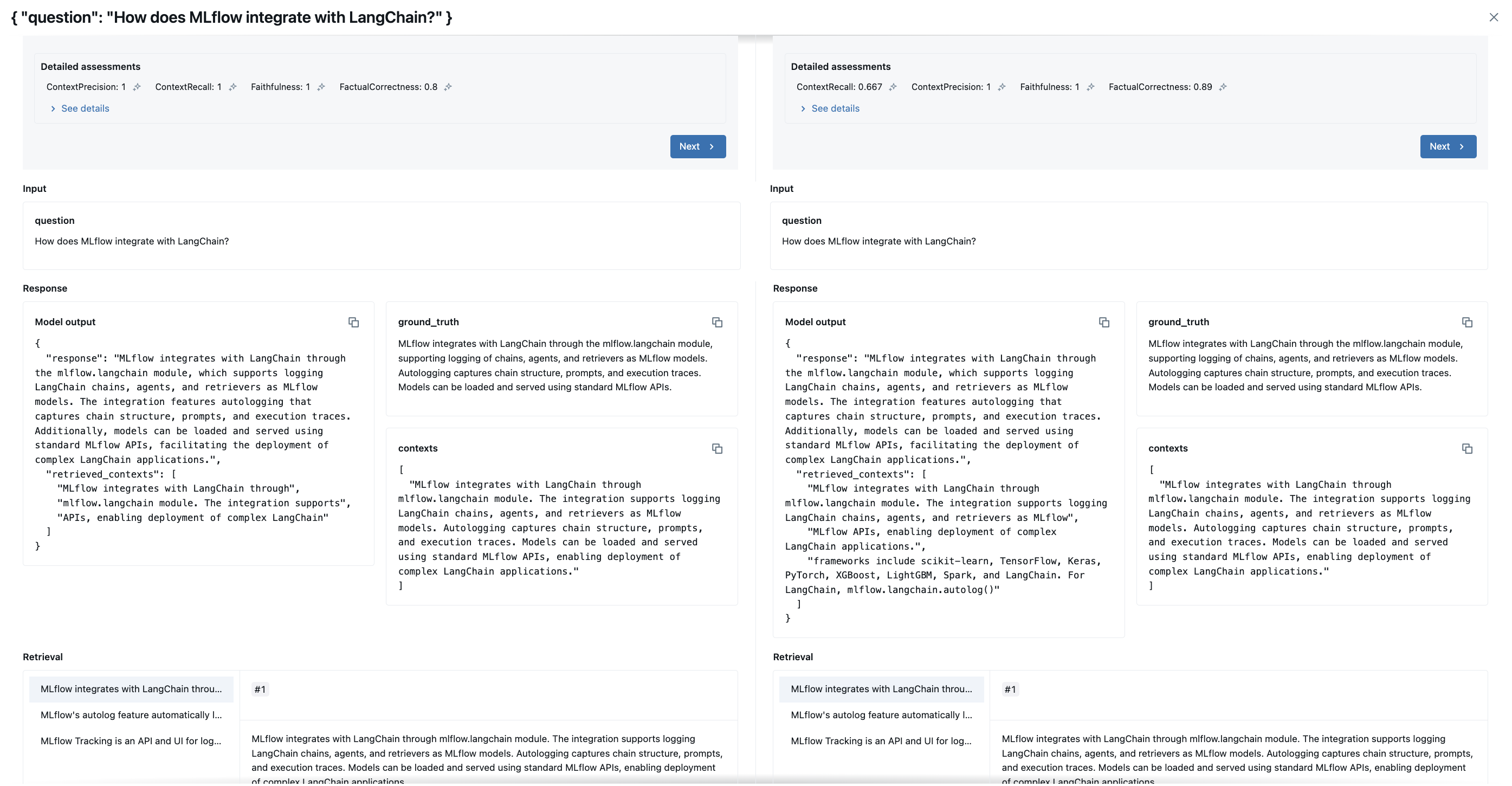 Figure 5: Comparison of individual question results for selected runs - detailed view showing metrics for each question.
Figure 5: Comparison of individual question results for selected runs - detailed view showing metrics for each question.
More from MLflow
This tutorial focused on RAG evaluation using RAGAS metrics. MLflow offers many more features for RAG or GenAI model management, including:
built-in metrics MLFlow predefined metrics for GenAI models
Guidelines-based LLM Scorers Guidelines-based LLM Scorers
from MLflow Documentation:
Guidelines is a powerful scorer class designed to let you quickly and easily customize evaluation by defining natural language criteria that are framed as pass/fail conditions. It is ideal for checking compliance with rules, style guides, or information inclusion/exclusion.
Guidelines have the distinct advantage of being easy to explain to business stakeholders ("we are evaluating if the app delivers upon this set of rules") and, as such, can often be directly written by domain experts.
- MCP server See the documentation on how to add MLflow MCP server in poular IDEs and Agentic conding tools: MLflow MCP Server
...and many more features. Explore the MLflow GenAI documentation for more details.
References, further reading
- the code for this tutorial is available on my GitHub: 2026-01-08-ragas-in-mlfow-rag-eval-demo
- MLflow Documentation
- Introduction to RAG with MLflow and LangChain - MLflow documentation - exemplary implementation of RAG with LangChain and MLflow (without RAGAS evaluation).
- GitHub - rag_evaluation_and_tracking - This project houses a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) LLM application built for robust and context-aware text generation. It leverages the combined power of LangChain for orchestration, MLflow for tracking and experimentation, DVC for version control, and RAGAS for evaluation.
