2023-01-18
Tools That Helps to Understand and Tweak Random Forest Classifier
Random Forest is a popular machine learning algorithm, known for its high accuracy and versatility. However, it can be challenging to understand the inner workings of the algorithm and tweak its parameters for optimal performance. In this article, we will explore some lesser-known but useful tools that can help you better understand and tweak your Random Forest classifier.
1. Feature Importance
One of the most important aspects of a Random Forest classifier is understanding the relative importance of the features used to make predictions. scikit-learn provides a built-in function to compute feature importance, feature_importances_. However, this method can be misleading for high-dimensional datasets or datasets with correlated features. A better alternative is permutation importance which can be calculated using the permutation_importance function in the sklearn.inspection module. This method randomly shuffles the values of a single feature and calculates the decrease in the model's performance, providing a more accurate measure of feature importance.
Another alternative is the SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) library, which allows for the calculation of feature importance in a more explainable way. It considers all possible coalitions of features and assigns a value to each feature based on its contribution to the prediction. For the tree methods there is a speed-optimized KernelShap and TreeShap - Two Most Popular Variations of the SHAP Method method to explain the tree-based models.
See: plot - Random Forest Feature Importance Chart using Python - Stack Overflow
2. Partial Dependence Plots
Partial dependence plots are a useful tool for visualizing the relationship between a feature and the model's prediction. They plot the average prediction of the model as a function of one feature, while holding the other features constant. scikit-learn provides a built-in function to generate partial dependence plots, plot_partial_dependence. However, this function only allows for the visualization of one or two features at a time. An alternative is the PDPbox library, which allows for the visualization of multiple features at once.
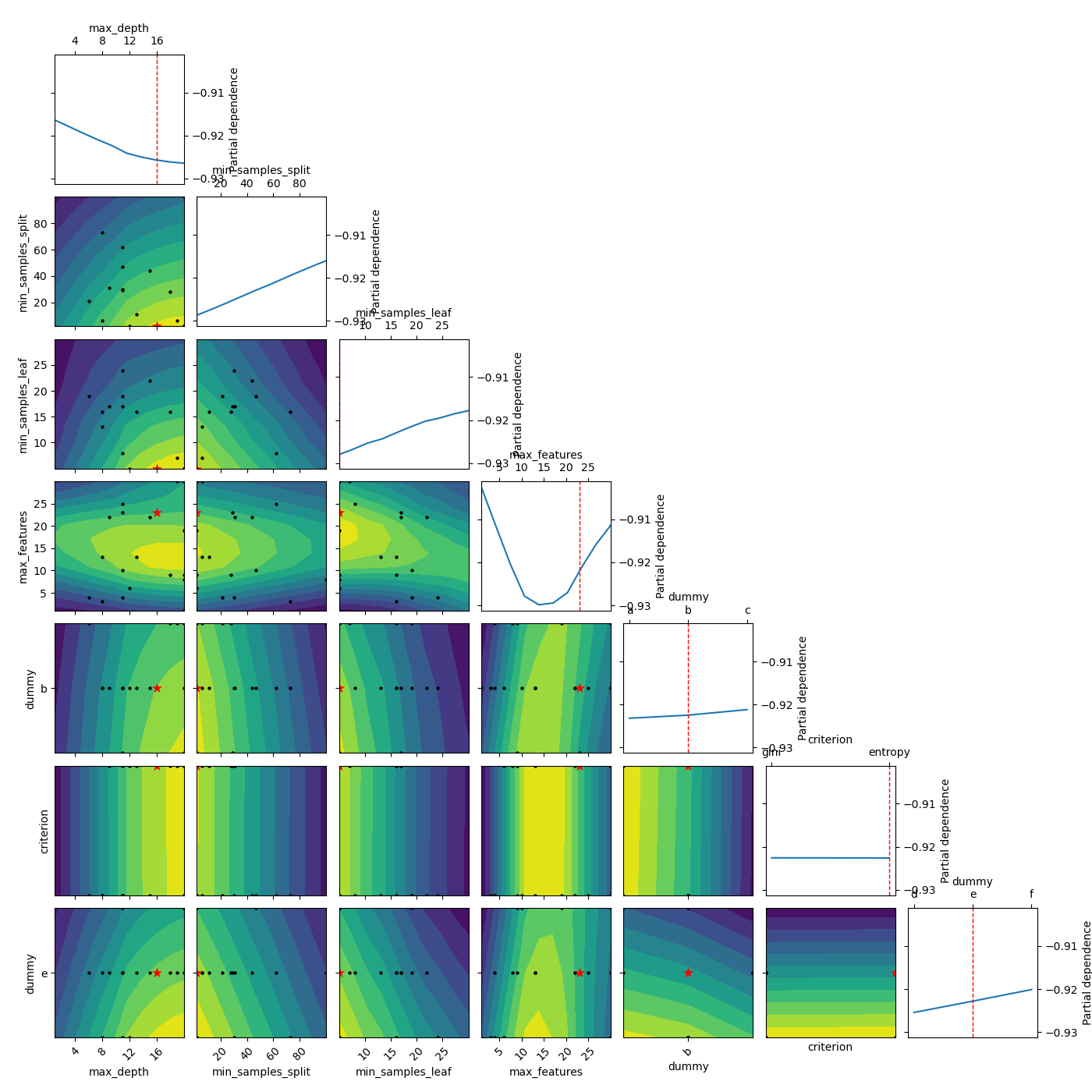
Figure 1. Example of Partial Dependence Plots with categorical values - plotted with scikit-optimize. (image source: scikit-optimize documentation)
3. Tree Interpreter
The treeinterpreter library provides an easy way to understand the predictions made by a Random Forest classifier. It decomposes the predictions of the ensemble into contributions from each individual tree, allowing you to understand the decision-making process of the model. This library can be used in combination with SHAP to understand how each feature contributes to the model's prediction.
See: Treeinterpreter - Interpreting Tree-Based Model's Prediction of Individual Sample [Python]
4. Random Forest Explorer
The Random Forest Explorer is an interactive tool that allows you to explore the decision boundaries of a Random Forest classifier. It is built on top of the bokeh library and provides a user-friendly interface for visualizing the predictions of the model.
Conclusion
Random Forest is a powerful machine learning algorithm, but it can be challenging to understand and tweak its behavior. The tools discussed in this article, such as feature importance, partial dependence plots, tree interpreter and Random Forest Explorer can help you better understand the inner workings of the model and make more informed decisions when tuning its parameters. These tools are lesser known but can be very useful in understanding and improving the performance of a Random Forest classifier.
Note that the above instructions are a general guide and you should check the specific instructions for your setup and the version of the package you are using.
References:
- 4.2. Permutation feature importance — scikit-learn 1.3.2 documentation
- GitHub - shap/shap: A game theoretic approach to explain the output of any machine learning model.
- GitHub - SauceCat/PDPbox: python partial dependence plot toolbox
- GitHub - andosa/treeinterpreter
- https://github.com/parrt/random-forest-explorer
-
dice-ml - Diverse Counterfactual Explanations for ML Models [Python]
Tags:
machine-learning
random-forest
xai