2023-08-24
Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) empowering LLMs
Understand innovative artificial intelligence framework that empower large language models (LLMs) by anchoring them to external knowledge sources with accurate, current information.
TLDR
Retrieval augmented generation refers to the method of enhancing a user's input to a large language model (LLM) such as ChatGPT by incorporating extra information obtained from an external source. This additional data can then be utilized by the LLM to enrich the response it produces.
- Introduction: Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- The Need for RAG in Large Language Models
- The 'Open Book' Approach of RAG
- Personalized and Verifiable Responses with RAG
- Challenges and Future Directions
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction: Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation, commonly referred to as RAG, and sometimes called Grounded Generation (GG), represents an ingenious integration of pretrained dense retrieval (DPR) and sequence-to-sequence models.
Transformer architecture (used in GPT models) is a member of sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) architectures. Seq2Seq models are designed to handle tasks that involve transforming an input sequence into an output sequence, such as machine translation, text summarization, and dialogue generation.
The process involves retrieving documents using DPR and subsequently transmitting them to a seq2seq model. Through a process of marginalization, these models then produce desired outputs. The retriever and seq2seq modules commence their operations as pretrained models, and through a joint fine-tuning process, they adapt collaboratively, thus enhancing both retrieval and generation for specific downstream tasks. This innovative artificial intelligence framework serves as a means to empower large language models (LLMs) by anchoring them to external knowledge sources. Consequently, this strategic approach ensures the availability of accurate, current information, thereby granting users valuable insights into the generative mechanisms of these models. For a comprehensive understanding of the RAG technique, we offer an in-depth exploration, commencing with a simplified overview and progressively delving into more intricate technical facets.
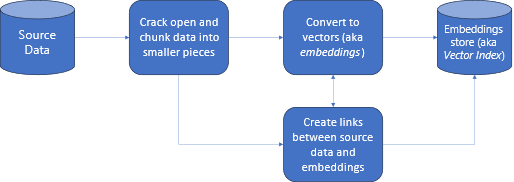
Figure 1. Data processing, storage and referencing in RAG method. Source: Microsoft
The Need for RAG in Large Language Models
Large language models, while powerful, can sometimes be inconsistent in their responses. They may provide accurate answers to certain questions but struggle with others, often regurgitating random facts from their training data. This inconsistency stems from the fact that LLMs understand the statistical relationships between words but not their actual meanings.
To address this issue, researchers have developed the RAG framework, which improves the quality of LLM-generated responses by grounding the model in external sources of knowledge. This approach not only ensures access to the most current and reliable facts but also allows users to verify the model's claims for accuracy and trustworthiness.
The 'Open Book' Approach of RAG
RAG operates in two main phases: retrieval and content generation. During the retrieval phase, algorithms search for and retrieve relevant snippets of information based on the user's prompt or question. These facts can come from various sources, such as indexed documents on the internet or a closed-domain enterprise setting for added security and reliability.
In the generative phase, the LLM uses the retrieved information and its internal representation of training data to synthesize a tailored answer for the user.
This approach is akin to an "open book" exam, where the model can browse through content in a book rather than relying solely on its memory.
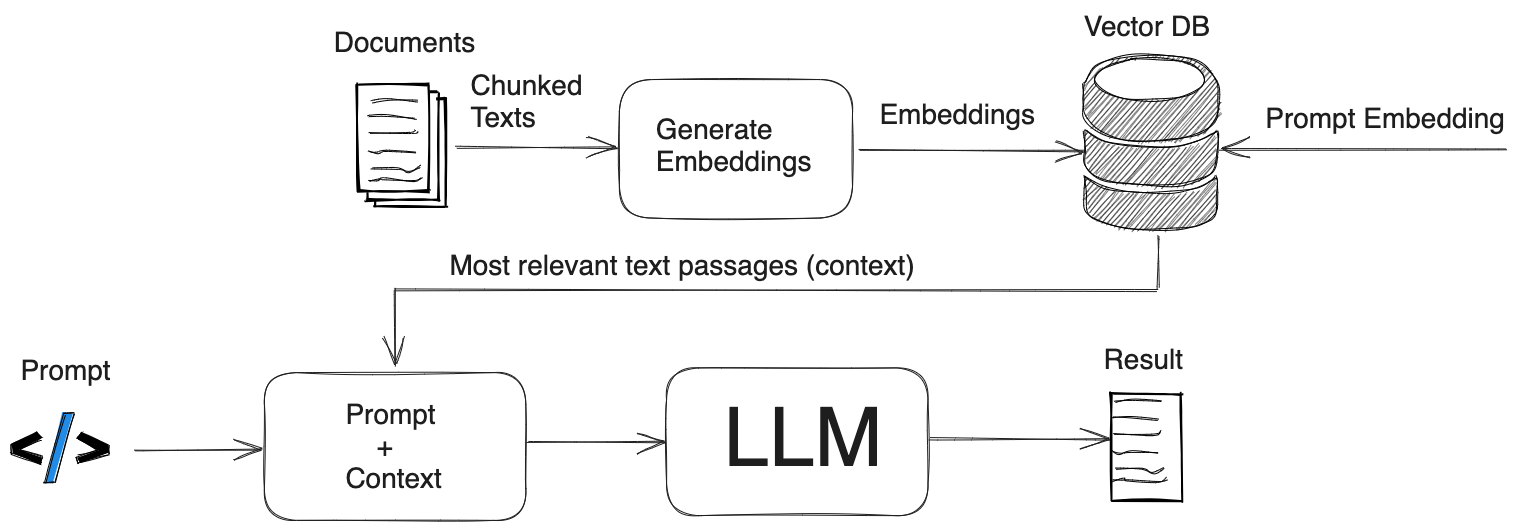 Figure 2. RAG operation. Information preparation and storage. Augmenting prompt with external information.
Figure 2. RAG operation. Information preparation and storage. Augmenting prompt with external information.
Personalized and Verifiable Responses with RAG
RAG allows LLM-powered chatbots to provide more personalized answers without the need for human-written scripts. By reducing the need to continuously train the model on new data, RAG can lower the computational and financial costs of running LLM-powered chatbots in an enterprise setting.
Moreover, RAG enables LLMs to generate more specific, diverse, and factual language compared to traditional parametric-only seq2seq models. This feature is particularly useful for businesses that require up-to-date information and verifiable responses.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its advantages, RAG is not without its challenges. For instance, LLMs may struggle to recognize when they don't know the answer to a question, leading to incorrect or misleading information. To address this issue, researchers are working on fine-tuning LLMs to recognize unanswerable questions and probe for more detail until they can provide a definitive answer.
Furthermore, there is ongoing research to improve both the retrieval and generation aspects of RAG. This includes finding and fetching the most relevant information possible and structuring that information to elicit the richest responses from the LLM.
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation offers a promising solution to the limitations of large language models by grounding them in external knowledge sources. By adopting RAG, businesses can achieve customized solutions, maintain data relevance, and optimize costs while harnessing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. As research continues to advance in this area, we can expect even more powerful and efficient language models in the future.
Any comments or suggestions? Let me know.
References
- Original paper Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks by Patrick Lewis et al. (available as paper with code)
- Exemplary notebooks on amazon Sagemaker:
- Python library with RAG implementation: GitHub - llmware-ai/llmware: Providing enterprise-grade LLM-based development framework, tools and fine-tuned models.
- Analytics: Vectorview
- Deep-dive into specific use-case of RAG with scaling in mind: Building RAG-based LLM Applications for Production (Part 1)
- Good section on possible improvements to RAG: Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): What, Why and How? | LLMStack
- General intro to RAG: How do domain-specific chatbots work? An Overview of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) | Scriv
- Optimization, async, using summaries: Secrets to Optimizing RAG LLM Apps for Better Performance, Accuracy and Lower Costs! | by Madhukar Kumar | madhukarkumar | Sep, 2023 | Medium
- Check the GitHub for the RAG-related projects: retrieval-augmented-generation · GitHub Topics
- Yet another RAG system - implementation details and lessons learned : r/LocalLLaMA
- Building and Evaluating Advanced RAG Applications - DeepLearning.AI - recent course from deeplearning.ai (Andrew Ng). Instructors: Jerry Liu and Anupam Datta.
- In this course, we’ll explore:
- Two advanced retrieval methods: Sentence-window retrieval and auto-merging retrieval that perform better compared to the baseline RAG pipeline.
- Evaluation and experiment tracking: A way evaluate and iteratively improve your RAG pipeline’s performance.
- The RAG triad: Context Relevance, Groundedness, and Answer Relevance, which are methods to evaluate the relevance and truthfulness of your LLM’s response.
- In this course, we’ll explore:
X::Techniques to Boost RAG Performance in Production
Edits:
- 2023-10-23 - added link to LLMStack
- 2023-11-06 - added TLDR section
- 2023-11-06 - added ToC
To cite this article:
@article{Saf2023Understanding,
author = {Krystian Safjan},
title = {Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) empowering LLMs},
journal = {Krystian's Safjan Blog},
year = {2023},
}
